Redis 01 - Introduction
I try to present an overview of Redis, its history, what it can do, how it works, in a very short introduction. I present briefly the performances, the optimizations, the savings.
You can find links to the related video recordings and printable materials at the end of this post.
- Video
- Origin
- In-Memory and persistency
- Highly optimized
- Key-datastructure store and multi-model
- Transactions and locks
- One of the biggest active and real community
- Linear scalability and high-availability
- Conclusion : the benefits of Redis
- Materials and Links
- Footnotes
Video
Origin
Redis means Remote Dictionnary Server.
It is an opensource project started in 2009 by Salvatore Sanfilippo, aka Antirez, in Sicily.
Its goals is to store application variables outside of the application.
Thus, the application can be restarted and can resume its work from its last status and several applications can manipulate the same shared variables.
From the very beginning, the clarity of the code, the simplicity to use and the completness of the documentation were a priority.

In-Memory and persistency
For such a goal, Redis needs to be extremely performant. This is an in-memory datastore, meaning that it stores and serve the data to and from memory. It could work without any attached disk. A disk can be added to persist the data, for durability, and this doesn’t need to be a fast disk.
Redis is so fast that it does never need a cache on top of it and it is often used and known as a cache on top of other relational and NoSQL databases to speed them up.
This is very important, unlike other databases, Redis does not store and serve the data from the disk using memory as a cache to speedup things, instead, Redis stores and serve the data directly from memory and eventually use a disk if persistency is needed.
Highly optimized
Memory is expensive and no-one can afford a waste of it, thus data are stored in Redis using efficient internal data structures to minimize the overhead at the byte level, sometimes at the bit level.
Most commands have a complexity of O(1), meaning that the execution time will be constant and predictable, whatever the dataset size is or will be.
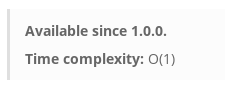
Each command is implemented to minimize the number of used CPU cycles. A single Redis instance can usually manage 25GB of data, at 25,000 ops/sec with a sub-millisecond latency, using…… only one single CPU core.
Key-datastructure store and multi-model
It is a key-value store. A single redis instance can store up to 2^31 keys. The value stored by a key is a datastructure. It can be as simple as a string or as complex as a JSON object, or a machine-learning model. Redis natively support 10 different datastructures and can be easily extended to support any kind of datastructure or feature by loading modules.
Redis also embed a simple but powerful messaging system to allow real time data processing and cross application communications.

When the developper manipulates a list in the application, he does not need to normalize or to serialize it before storing it. This makes the source code simplier and more robust but also faster to execute and to write.
Transactions and locks
Redis also support transactions and consistency, of course. More than 40 different languages support Redis, not only developper languages such a C, C++, NodeJS, Java, but also data analysts languages such as R, Python or Scala.

One of the biggest active and real community
Redis is so popular that the community is rich of a lot of different user profiles. It is easy to find the answer to a question about Redis on internet or to hire Redis experts. Redis has one of the biggest real community over the world, with a lot of contributors.
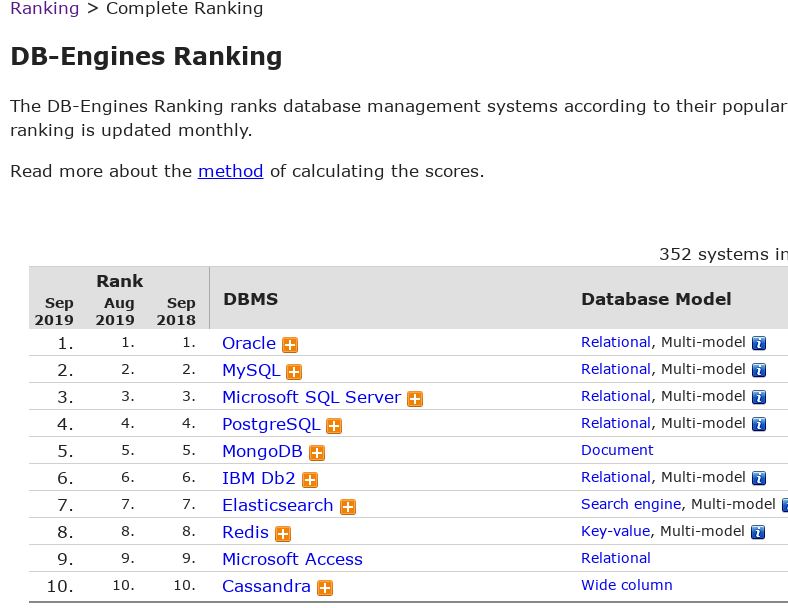
In the top 100 github projects In the top 10 databases in DB-engines
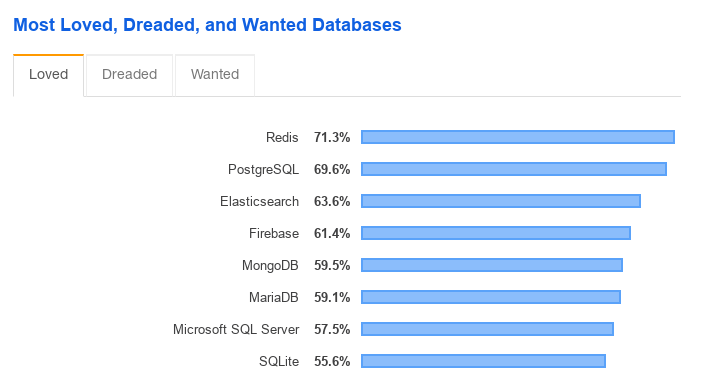
Most launched docker container from dockerhub Most loved database of StackOverflow members for 3 years
Linear scalability and high-availability
Redis can secure data access with high-availability by configuring Redis instances as replica of other Redis instances.
Redis can also scale linearly without downtime by sharding data across several redis instances on several servers. Redis is used everywhere, in nearly every company from the smallests to the biggests. It is used as a primary database to power core business, critical data processing and storage architectures.
Conclusion : the benefits of Redis
Redis usually reduces ownership costs, both on the infrastructure hardware, by optimizing the hardware usage, and on the human time. It also greatly improves the performances of the applications, the consistency and safety of the data.
Materials and Links
| Link | Description |
|---|---|
| Video | Video presentation |
| Google results for Redis | |
| Linkedin results for Redis skills1 | |
| github | Github redis project ranking |
| stackoverflow | Stackoverflow survey |
| dbengines | DB-engines ranking |
| datastructures | Redis datastructures list |
| pubsub | Redis messaging presentation |
| transactions | Redis transactions presentation |
| modules | Redis modules presentation |
| moduleshub | Redis modules list |
| http://redis.io | Redis project page |
Footnotes
-
You need to login on LinkedIn to see the page ↩